Washable, Wearable Battery-Like Devices Could be Woven Directly Into Clothes
Green Material For Refrigeration Identified
‘Magnetic Graphene’ Flips Between Insulator and Conductor
Mystery Orbits in Outermost Reaches of Solar System Not Caused by ‘Planet Nine’
AI System May Accelerate Search For Cancer Discoveries
Giant Planets Around Young Star Raise Questions About How Planets Form
Researchers have identified a young star with four Jupiter and Saturn-sized planets in orbit around it, the first time that so many massive planets have been detected in such a young system. The system has also set a new record for the most extreme range of orbits yet observed: the outermost planet is more than…
Sicilian Amber in Western Europe Pre-Dates Arrival of Baltic Amber by at Least 2,000 Years
Amber and other unusual materials such as jade, obsidian and rock crystal have attracted interest as raw materials for the manufacture of decorative items since Late Prehistory and, indeed, amber retains a high value in present-day jewellery. ‘Baltic’ amber from Scandinavia is often cited as a key material circulating in prehistoric Europe, but in a…
Household Phenomenon Observed by Leonardo da Vinci Finally Explained
An everyday occurrence spotted when we turn on the tap to brush our teeth has baffled engineers for centuries—why does the water splay when it hits the sink before it heads down the plughole? Famous inventor and painter Leonardo da Vinci documented the phenomenon, now known as a hydraulic jump, back in the 1500s. Hydraulic…
Low-Cost Plastic Sensors Could Monitor a Range of Health Conditions
An international team of researchers have developed a low-cost sensor made from semiconducting plastic that can be used to diagnose or monitor a wide range of health conditions, such as surgical complications or neurodegenerative diseases. The sensor can measure the amount of critical metabolites, such as lactate or glucose, that are present in sweat, tears,…
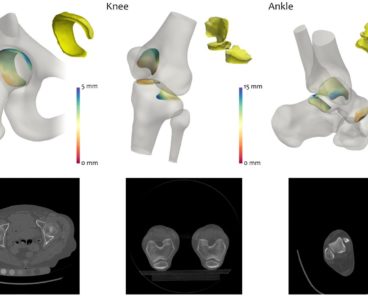
New 3D Imaging Analysis Technique Could Lead to Improved Arthritis Treatment
An algorithm to monitor the joints of patients with arthritis, which could change the way that the severity of the condition is assessed, has been developed by a team of engineers, physicians and radiologists led by the University of Cambridge. The technique, which detects tiny changes in arthritic joints, could enable greater understanding of how…
Multiple Metals–and Possible Signs of Water–Found in Unique Exoplanet
An international team of researchers has identified ‘fingerprints’ of multiple metals in one of the least dense exoplanets ever found. The team, from the University of Cambridge and the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) in Spain, used the Gran Telescopio Canarias (GTC) to observe WASP-127b, a giant gaseous planet with partly clear skies and…
Study Finds Two Ancient Ancestries ‘Reconverged’ With Settling of South America
Taming the Multiverse: Stephen Hawking’s Final Theory About the Big Bang
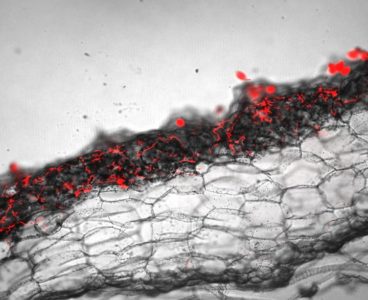
Research Shows First Land Plants Were Parasitized by Microbes
By studying liverworts – which diverged from other land plants early in the history of plant evolution – researchers from the Sainsbury Laboratory at the University of Cambridge have found that the relationship between plants and filamentous microbes not only dates back millions of years, but that modern plants have maintained this ancient mechanism to…
Beetle Scales Inspire Ultra-White Coating
Researchers have developed a super-thin, non-toxic, lightweight, edible ultra-white coating that could be used to make brighter paints and coatings, for use in the cosmetic, food, or pharmaceutical industries. The material — which is 20 times whiter than paper — is made from non-toxic cellulose and achieves such bright whiteness by mimicking the structure of…
Chain Reaction of Fast-Draining Lakes Poses New Risk for Greenland Ice Sheet
A growing network of lakes on the Greenland ice sheet has been found to drain in a chain reaction that speeds up the flow of the ice sheet, threatening its stability. Researchers from the UK, Norway, US and Sweden have used a combination of 3D computer modelling and real-world observations to show the previously unknown,…
Beetle-Inspired Ultra-White Coating
Rare Mineral Discovered in Plants for First Time
Scientists at Sainsbury Laboratory Cambridge University have found that the mineral vaterite, a form (polymorph) of calcium carbonate, is a dominant component of the protective silvery-white crust that forms on the leaves of a number of alpine plants, which are part of the Garden’s national collection of European Saxifraga species. Naturally occurring vaterite is rarely…
Think of Honeybees as ‘Livestock,’ Not Wildlife, Argue Experts
The ‘die-off’ events occurring in honeybee colonies that are bred and farmed like livestock must not be confused with the conservation crisis of dramatic declines in thousands of wild pollinator species, say Cambridge researchers. Writing in the journal Science, the conservationists argue there is a “lack of distinction” in public understanding – fuelled by misguided charity…
AI ‘Scientist’ Finds Toothpaste Ingredient May Help Fight Drug-resistant Malaria
Harnessing the Power of Algae: New, Greener Fuel Cells Move Step Closer to Reality
New Brain Mapping Technique Highlights Relationship Between Connectivity and IQ
Graphene Circuits Printed onto Fabric Can Survive 20 Washes
Researchers have successfully incorporated washable, stretchable, and breathable electronic circuits into fabric, opening up new possibilities for smart textiles and wearable electronics. The circuits were made with cheap, safe, and environmentally friendly inks, and printed using conventional inkjet printing techniques. The researchers, from the University of Cambridge, working with colleagues in Italy and China, have…
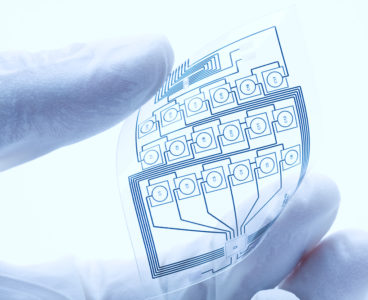
Fully Integrated Circuits Printed Directly Onto Fabric
Researchers have successfully incorporated washable, stretchable and breathable electronic circuits into fabric, opening up new possibilities for smart textiles and wearable electronics. The circuits were made with cheap, safe and environmentally friendly inks, and printed using conventional inkjet printing techniques. The researchers, from the University of Cambridge, working with colleagues in Italy and China, have…