There’s a joke by comedian Steven Wright that goes, “You can’t have everything. Where would you put it?” Users of advanced computing can likely relate to this. The exponential growth of data poses a steep challenge to efforts for its reliable storage. For over 12 years, the Ranch system at the Texas Advanced Computing Center…
Measurement of Semiconductor Material Quality Has Gotten 100,000 Times More Sensitive
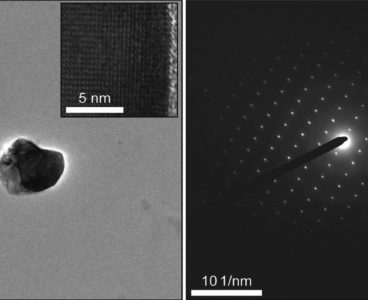
The enhanced power of the new measuring technique to characterize materials at scales much smaller than any current technologies will accelerate the discovery and investigation of 2D, micro- and nanoscale materials. Being able to accurately measure semiconductor properties of materials in small volumes helps engineers determine the range of applications for which these materials may…
Two New Planets Discovered Using Artificial Intelligence
Solar-Powered Moisture Harvester Collects and Cleans Water From Air
Access to clean water remains one of the biggest challenges facing humankind. A breakthrough by engineers at The University of Texas at Austin may offer a new solution through solar-powered technology that absorbs moisture from the air and returns it as clean, usable water. The breakthrough, described in a recent issue of the journal Advanced…
New Material Offers More Secure Computing
As computers advance, encryption methods currently used to keep everything from financial transactions to military secrets secure might soon be useless, technology experts warn. Reporting in the journal Nature, a team of physicists and engineers led by University of Texas at Austin physics professor Xiaoqin Elaine Li report they have created a material with light-emitting…
New Computer Modeling Approach Could Improve Understanding of Megathrust Earthquakes
Years before the devastating Tohoku earthquake struck the coast of Japan in 2011, the Earth’s crust near the site of the quake was starting to stir. Researchers at The University of Texas at Austin are using computer models to investigate if tiny tremors detected near the site of the quake could be connected to the…
Where Water Goes After Fracking is Tied to Earthquake Risk
In addition to producing oil and gas, the energy industry produces a lot of water, about 10 barrels of water per barrel of oil on average. New research led by The University of Texas at Austin has found that where the produced water is stored underground influences the risk of induced earthquakes. Beyond supporting the…
Nationwide High-intensity Laser Network Finds a Home
The University of Texas at Austin will be a key player in LaserNetUS, a new national network of institutions operating high-intensity, ultrafast lasers. The overall project, funded over two years with $6.8 million from the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Fusion Energy Sciences, aims to help boost the country’s global competitiveness in high-intensity laser…
Newly Described Fossils Could Help Reveal Why Some Dinos Got so Big
By the time non-avian dinosaurs went extinct, plant-eating sauropods like the Brontosaurus had grown to gargantuan proportions. Weighing in as much as 100 tons, the long-neck behemoths are the largest land animals to ever walk the earth. How they grew so large from ancestors that were small enough to be found in a modern-day petting…
Common Weed Killer Linked to Bee Deaths
The world’s most widely used weed killer may also be indirectly killing bees. New research from The University of Texas at Austin shows that honey bees exposed to glyphosate, the active ingredient in Roundup, lose some of the beneficial bacteria in their guts and are more susceptible to infection and death from harmful bacteria. Scientists…
UT Engineers Develop First Method for Controlling Nanomotors
New Cancer Treatment Uses Enzymes to Boost Immune System and Fight Back
Researchers at The University of Texas at Austin have developed a new approach to treating cancer using enzyme therapy. The enzyme, PEG-KYNase, does not directly kill cancer cells but instead empowers the immune system to eradicate unwanted cells on its own. PEG-KYNase is designed to degrade kynurenine, a metabolite produced by numerous tumors that suppresses…
Three Previously Unknown Ancient Primates Identified
Fish’s Use of Electricity Might Shed Light on Human Illnesses
Deep in the night in muddy African rivers, a fish uses electrical charges to sense the world around it and communicate with other members of its species. Signaling in electrical spurts that last only a few tenths of a thousandth of a second allows the fish to navigate without letting predators know it is there.…
Possible Link Found Between Diabetes and Common White Pigment
In a pilot study by a team of researchers at The University of Texas at Austin, crystalline particles of titanium dioxide — the most common white pigment in everyday products ranging from paint to candies — were found in pancreas specimens with Type 2 diabetes, suggesting that exposure to the white pigment is associated with…
New Research Suggests that Dawn of Plate Tectonics could have Turned Earth into Snowball
A research duo from The University of Texas at Austin and UT Dallas have put forward a hypothesis that links the dawn of plate tectonics with “snowball Earth”–a period of climate change that sent the planet into a deep freeze that lasted millions of years. They expect their hypothesis to generate controversy. Geologists usually place…
Highly Elastic Biodegradable Hydrogel Used for Bio-Printing New Tissues
Researchers at The University of Texas at Arlington have developed a highly elastic biodegradable hydrogel for bio-printing of materials that mimic natural human soft tissues. Bio-printing uses live cells within the scaffolding of the new tissues and could potentially transform cell printing. A provisional patent application has been filed on this new material, which will…
Anti-Alcoholism Drug Shows Promise in Animal Models
Sunlight and Hydrogels Used to Purify Water
The ability to create clean, safe drinking water using only natural levels of sunlight and inexpensive gel technology could be at hand, thanks to an innovation in water purification. According to the United Nations, 30,000 people die each week from the consumption and use of unsanitary water. Although the vast majority of these fatalities occur…
“Nanotweezers” Pave Way for New Innovations in Medicine, Mobile Tech
It’s difficult to conceptualize a world where humans could casually manipulate nanoscale objects at will or even control their own biological matter at a cellular level with light. But that is precisely what Yuebing Zheng, assistant professor of mechanical engineering at The University of Texas at Austin, is working toward with his “nanotweezers” — a…
Ultra-thin Memory Storage Device Paves Way for More Powerful Computing
Engineers worldwide have been developing alternative ways to provide greater memory storage capacity on even smaller computer chips. Previous research into two-dimensional atomic sheets for memory storage has failed to uncover their potential — until now. A team of electrical engineers at The University of Texas at Austin, in collaboration with Peking University scientists, has…
Promise of New Antibiotics Lies With Shackling Tiny Toxic Tetherballs to Bacteria
Biologists at The University of Texas at Austin have developed a method for rapidly screening hundreds of thousands of potential drugs for fighting infections, an innovation that holds promise for combating the growing scourge of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. The method involves engineering bacteria to produce and test molecules that are potentially toxic to themselves. A description…
New Research Improves Understanding of Ancient Landscapes
Geologists use zircon mineral grains to reconstruct what the Earth and its landscapes looked like in ancient times. These microscopic grains, commonly the width of a human hair, record detailed information on when and where they formed, making them a standard tool for studying how our planet has changed through the ages. A new study…
Golden Nanopill Provides Superior Drug Delivery
Imagine a microscopic gold pill that could travel to a specific location in your body and deliver a drug just where it is needed. This is the promise of plasmonic nanovesicles. These minute capsules can navigate the bloodstream, and, when hit with a quick pulse of laser light, change shape to release their contents. It…
Ancient Enzyme Could Boost Power of Liquid Biopsies
Scientists are developing a set of medical tests called liquid biopsies that can rapidly detect the presence of cancers, infectious diseases and other conditions from only a small blood sample. Researchers at The University of Texas at Austin are developing a new tool for liquid biopsy that could soon provide doctors with a more complete picture…