Genomenon Inc., an AI-driven genomics company, announces the completion of a $20 million Series B financing round. The funds will expand the company’s commercial operations and the development of its genomic data hub, which serves genetic testing labs, hospitals, pharmaceutical, and biopharma companies. Genomenon leverages AI (Artificial Intelligence) to organize the world’s genomic knowledge and…
R&D 100 winner of the day: ML-GA
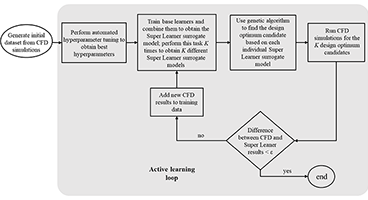
Argonne’s ML-GA software technology provides a unique artificial intelligence-driven optimization suite to shrink the industrial design cycle for product development across a variety of markets. The basic principle behind ML-GA is the coupling of machine learning (ML)-based fast-running surrogate models (in place of computationally expensive simulations) with a global optimization technique (in this case, a…
R&D collaborations looking to build expertise, in this week’s R&D power index
The R&D World Index (RDWI) for the week ending February 18, 2022, closed at 5,075.11 for the 25 companies in the RDWI. The Index was down -2.18% (or 113.00 basis points) from the week ending February 11, 2022. The stock of nine RDWI members gained value from 0.96% (Novartis) to 6.14% (Cisco). The stock of…
Algorithm could shorten quality testing, research in many industries by months
From Sandia National Laboratories A machine-learning algorithm developed at Sandia National Laboratories could provide auto manufacturing, aerospace and other industries a faster and more cost-efficient way to test bulk materials. The technique was published recently in the scientific journal Materials Science and Engineering: A. Production stoppages are costly. So, manufacturers screen materials like sheet metal…
R&D 100 winner of the day: SmartTensors AI Platform
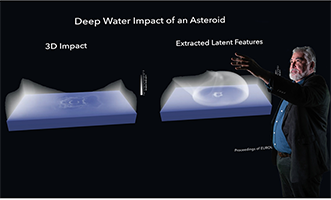
The SmartTensors AI Platform, developed at Los Alamos National Laboratory, is a scalable, unsupervised machine-learning software suite capable of identifying, extracting essential hidden features, and efficiently compressing information in massive datasets. SmartTensors autonomously analyzes and discovers hidden features, signatures and patterns otherwise undetectable and buried in tens of terabytes of data. Big data surrounds us…
Rising inflation rates undermine economic growth, in this week’s R&D Power Index
The R&D World Index (RDWI) for the week ending January 21, 2022, closed at 5,208.27 for the 25 companies in the RDWI. The Index was down -5.66% (or 312.43 basis points) from the week ending January 14, 2022. The stock of only one RDWI member gained value at 0.42% (AstraZeneca). The stock of 24 RDWI…
Proscia and Datavant partner to connect pathology data with health data ecosystem for life sciences R&D
Proscia, the digital and computational pathology solutions provider, and Datavant, which securely connects organizations with health data, have announced a partnership that will provide life sciences companies with digitized pathology data to power the development of novel therapeutics and diagnostics. The partnership brings together Datavant’s privacy-preserving connectivity technology and the largest U.S. health data ecosystem…
Sony and Foxconn developing EVs, in this week’s R&D Power Index
The R&D World Index (RDWI) for the week ending January 7, 2022, closed at 5,472.25 for the 25 companies in the RDWI. The Index was down -2.79% (or -157.25 basis points) from the week ending December 31, 2021. The stock of 16 RDWI members gained value from 0.17% (Roche Holdings AG) to 17.67% (Ford Motor).…
R&D winner of the day: Small World AI
LocationMind and the University of Tokyo’s Small World AI, an artificial intelligence (AI) technologies integration system, has provided insights in various fields, especially for the COVID-19 situation in Japan. GeoSpatial data has played an important role in estimating the threats and impact of the pandemic and further aided stakeholders in swift decision-making. In light of…
LLNL establishes AI Innovation Incubator to advance artificial intelligence for applied science
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) has established the AI Innovation Incubator (AI3), a collaborative hub aimed at uniting experts in artificial intelligence (AI) from LLNL, industry and academia to advance AI for large-scale scientific and commercial applications. LLNL has entered into new memoranda of understanding with Google, IBM and NVIDIA, with plans to use the…
R&D 100 winner of the day: Forager
Brightseed’s Forager is an AI-based scientific platform that maps the chemical complexity of plants to the biological complexity in humans. Through this map, Forager identifies bioactive compounds that solve unmet human health needs, linking distinct compounds from specific plants to fundamental biological processes that drive our health. Nature has evolved a wealth of natural compounds…
SwRI developing connected vehicle data exchange platform for Florida Department of Transportation
From Southwest Research Institute Southwest Research Institute is leading an $8 million project to develop a data exchange platform enabling the Florida Department of Transportation (FDOT) to analyze road conditions in real-time and communicate important travel information to the traveling public, state/local government entities, private sector partners and other stakeholders. In addition to real-time analysis,…
Proscia announces Artificial Intelligence breakthrough in melanoma detection
Proscia, a provider of digital and computational pathology solutions, has released study results on new technology that leverages artificial intelligence (AI) to automatically detect melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, with a high degree of accuracy. The findings illustrate the promise of AI to deliver faster diagnoses, improve patient outcomes and optimize laboratory economics…
Vicarious Surgical to debut on NYSE as a disruptive surgical robotics company
Vicarious Surgical, a next-generation robotics technology company seeking to improve both cost and efficiency of surgical procedures as well as patient outcomes, has announced that the shareholders of D8 Holdings have approved the previously announced business combination at the shareholder meeting held this week. The business combination is expected to provide approximately $220 million in…
DOE’s Argonne National Laboratory and Hewlett Packard Enterprise ready for exascale era with new testbed supercomputer
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory (ANL) and Hewlett Packard Enterprise unveiled a new testbed supercomputer to prepare critical workloads for future exascale systems that will deliver up to 4x faster performance than Argonne’s current supercomputers. The new system, which Argonne has named Polaris, will be built by HPE, and hosted and…
Digital Science launches Dimensions Life Sciences & Chemistry
Digital Science announces the launch of a new version of its popular Dimensions platform – Dimensions Life Sciences & Chemistry (Dimensions L&C) – focused on life sciences and chemistry research activities. Dimensions L&C analyzes more than 120 million scientific publications, millions of patents, grants and clinical trial documents. It is both larger than other databases,…
System trains drones to fly around obstacles at high speeds
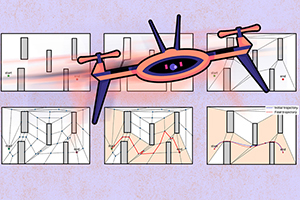
Written by Jennifer Chu, MIT News Office If you follow autonomous drone racing, you likely remember the crashes as much as the wins. In drone racing, teams compete to see which vehicle is better trained to fly fastest through an obstacle course. But the faster drones fly, the more unstable they become, and at high…
Dotmatics to implement Croda’s R&D digital program: AI and data mining
Dotmatics, a scientific informatics software and services company, announces it has been selected by Croda International to implement its Research and Development (R&D) digital program. Croda creates, makes and sells specialty chemicals that are used by industries and consumers. This new project will deepen Croda’s ability to innovate collaboratively, both internally and externally, delivering enhanced…
SwRI awarded $34M contract to support U.S. Army Ground Vehicle Systems Center
Southwest Research Institute received an indefinite delivery, indefinite quantity (IDIQ) contract valued at up to $34 million over five years to support the US. Army Ground Vehicle Systems Center through research and development of autonomous and robotic vehicles. “SwRI is proud to continue developing the latest autonomous and robotic systems for the U.S. military,” said…
Advancing future energy technologies with more accurate electrochemical simulations
Accurate predictive simulations of the electrochemical reactions that power solar fuel generators, fuel cells and batteries could advance these technologies through improved material design, and by preventing detrimental electrochemical processes, such as corrosion. However, electrochemical reactions are so complex that current computational tools can only model a fraction of all relevant factors at one time…
SRI International and Sanofi enter a drug discovery and research collaboration
SRI International (SRI) has entered a research collaboration with Sanofi, leveraging SRI’s SynFini artificial intelligence (AI)-guided, automated synthetic-chemistry system platform. The collaboration will discover and develop lead candidates in multiple high-profile drug-discovery programs at Sanofi. SRI’s SynFini platform combines AI and automation to accelerate small molecule drug discovery and development, and thereby bring new drugs…
Can artificial intelligence open new doors for materials discovery?
By Dave Bukey The future of clean energy is hot. Temperatures hit 800° C in parts of solar energy plants and advanced nuclear reactors. Finding materials that can stand that type of heat is tough. So experts look to Mark Messner for answers. A principal mechanical engineer at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne…
Nagoya Institute of Technology and NGK form “NGK Environment Innovation Laboratory”
Nagoya Institute of Technology (NITech) and NGK INSULATORS (NGK), both based in Nagoya, Japan, have established the NGK Environment Innovation Laboratory on the NITech campus. This collaboration between the private sector and academia will work on creating innovative next-generation products that contribute to a significant reduction of greenhouse gases, such as materials for next-generation power…
ACD/Labs joins Science Data Experts helping companies implement machine learning and artificial intelligence technologies
ACD/Labs, a provider of scientific informatics technologies for molecular characterization, has announced a partnership with Science Data Experts (SDE). Together, ACD/Labs and SDE will use their experience and expertise to enable life sciences organizations to implement a variety of machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to accelerate innovation in R&D. The partnership will…
108Labs is building the world’s first cell cultured human milk factory in North Carolina
Eighteen months after creating the world’s first cell cultured human milk, 108Labs is now focused on accelerating the field from lab to factory by building and programming the world’s first autonomous Cellufacturing facility and artificial intelligence platform for production of cell cultured human milk in the birthplace of biosynthetic human milk, Hillsborough, N.C. With an…